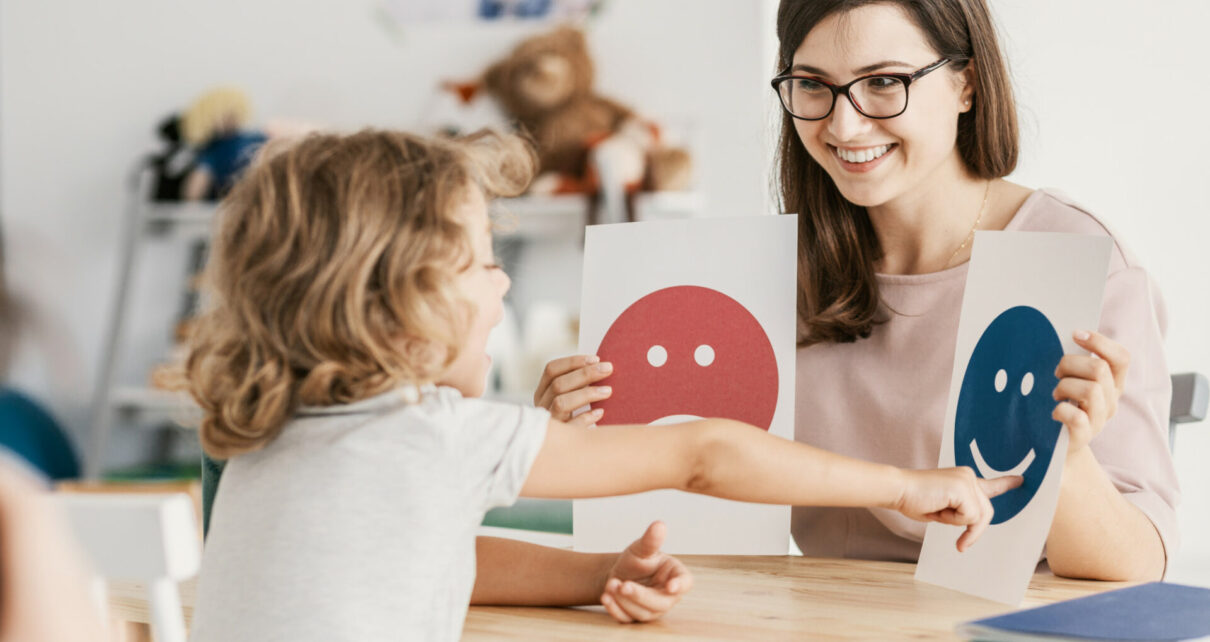
Welcome to the world of Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy, where understanding the basics is essential. ABA therapy is a widely recognized and evidence-based treatment approach that focuses on improving specific behaviors in individuals with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) or other developmental disabilities. In this article, we delve into the fundamental principles and concepts behind ABA therapy to provide you with a comprehensive understanding of its effectiveness and impact.
Through the use of systematic observations and data analysis, ABA therapists create personalized treatment plans tailored to the unique needs of each individual. By breaking down complex behaviors into smaller components and systematically reinforcing positive behaviors, ABA therapy aims to facilitate skill development, enhance communication, and reduce problem behaviors.
Whether you are a parent, caregiver, or educator seeking to expand your knowledge of ABA therapy or someone interested in pursuing a career in the field, this article serves as a valuable resource to grasp the essentials of this therapeutic approach. Join us as we unravel the core principles and techniques employed in ABA therapy, providing you with a solid understanding of how it can positively impact the lives of individuals with ASD.
What is Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy?
Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy is a scientifically validated approach that focuses on understanding and improving behavior. It is based on the principles of learning and behavior, which have been extensively studied and proven effective in various settings. ABA therapy aims to increase desirable behaviors while minimizing problem behaviors through the application of evidence-based strategies.
One of the key features of ABA therapy is its emphasis on data collection and analysis. ABA therapists systematically observe and record behavior to identify patterns and determine the factors that contribute to specific behaviors. This data-driven approach allows therapists to develop targeted interventions that are tailored to the unique needs of each individual.
ABA therapy is not limited to individuals with autism spectrum disorder (ASD). It can also be applied to individuals with other developmental disabilities, such as attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), intellectual disabilities, and behavioral challenges. ABA therapy is a flexible and adaptable approach that can be modified to suit the specific needs and goals of each individual.
The Principles of ABA Therapy
The foundation of ABA therapy is built upon a set of principles that guide the assessment and treatment process. These principles are derived from the science of behavior analysis and provide a framework for understanding and modifying behavior.
One of the core principles of ABA therapy is positive reinforcement. Positive reinforcement involves providing rewards or incentives for desired behaviors, which increases the likelihood of those behaviors occurring again in the future. By identifying and reinforcing positive behaviors, ABA therapy promotes skill development and encourages individuals to engage in appropriate behaviors.
Another principle of ABA therapy is prompting and fading. Prompting involves providing cues or assistance to help individuals perform a desired behavior. As the individual becomes more proficient, the prompts are gradually reduced or faded out. This gradual fading allows individuals to develop independent skills and reduces reliance on prompts.
The ABCs of Behavior Analysis
In behavior analysis, the ABC model is used to understand the antecedents, behaviors, and consequences of a particular behavior. This model helps identify the factors that trigger and maintain specific behaviors, providing valuable insights for intervention planning.
The antecedent refers to the events or circumstances that occur immediately before a behavior. Antecedents can be environmental factors, such as a specific situation or a particular request. By identifying the antecedents that precede problem behaviors, ABA therapists can develop strategies to modify or eliminate those triggers.
The behavior is the specific action or response exhibited by an individual. It can be an observable behavior, such as talking, writing, or hitting. ABA therapists carefully observe and analyze behaviors to identify patterns and determine the function or purpose of those behaviors.
The consequence refers to the events or stimuli that follow a behavior. Consequences can be positive or negative, and they influence the likelihood of the behavior occurring again in the future. ABA therapists use consequences strategically to reinforce positive behaviors and reduce problem behaviors.
The Importance of Functional Assessment
Before developing a treatment plan, ABA therapists conduct a functional assessment to gain a comprehensive understanding of the individual’s behavior. A functional assessment involves gathering information about the antecedents, behaviors, and consequences of the target behavior.
The purpose of a functional assessment is to determine the function or purpose that the behavior serves for the individual. Behaviors can serve various functions, such as seeking attention, escaping a demand, obtaining a desired item, or self-stimulation. By identifying the function of the behavior, ABA therapists can develop interventions that address the underlying cause of the behavior.
Functional assessments can be conducted through direct observation, interviews with caregivers or teachers, and the use of standardized assessment tools. The data collected during the functional assessment informs the development of a personalized treatment plan that targets the specific behavior and its underlying function.
Common Techniques Used in ABA Therapy
ABA therapy utilizes a variety of techniques and strategies to promote behavior change and skill development. These techniques are tailored to the individual’s needs and goals, and they are implemented consistently to achieve desired outcomes.
One commonly used technique in ABA therapy is discrete trial training (DTT). DTT involves breaking down complex skills into smaller, more manageable components. Each component is taught through a series of structured trials, with reinforcement provided for correct responses. DTT is particularly effective for teaching new skills and promoting skill generalization.
Another technique used in ABA therapy is naturalistic teaching. Naturalistic teaching involves embedding learning opportunities into everyday activities and environments. This approach focuses on promoting skills in a natural and functional context, enhancing the individual’s ability to apply learned skills in real-life situations.
ABA Therapy for Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder
ABA therapy has been widely recognized as an effective intervention for children with autism spectrum disorder (ASD). It can help children develop essential skills, such as communication, social interaction, and self-care, while reducing problem behaviors that may interfere with daily functioning.
For children with ASD, ABA therapy typically involves intensive and structured intervention delivered by trained professionals. The therapy is tailored to the individual’s specific needs and goals, and it is implemented in various settings, such as home, school, or clinic.
ABA therapy for children with ASD focuses on targeting core deficits, such as social communication, joint attention, play skills, and adaptive behaviors. It utilizes evidence-based strategies, such as visual supports, social stories, and reinforcement systems, to promote skill acquisition and generalization.
ABA Therapy for Other Behavioral Disorders and Challenges
While ABA therapy is commonly associated with autism spectrum disorder, it can also be beneficial for individuals with other behavioral disorders and challenges. ABA techniques can be applied to address a wide range of behaviors, including aggression, self-injury, noncompliance, and attention difficulties.
In addition to individuals with diagnosed disorders, ABA therapy can also benefit individuals who exhibit challenging behaviors that interfere with their daily functioning or quality of life. The principles and techniques of ABA therapy can be modified and adapted to address specific behaviors and promote positive change.
The Role of the ABA Therapist
The ABA therapist plays a crucial role in the assessment and implementation of ABA therapy. As highly trained professionals, ABA therapists possess the knowledge and skills to assess behavior, develop treatment plans, and implement interventions effectively.
ABA therapists conduct thorough assessments to identify target behaviors, determine their functions, and establish baseline data. Based on the assessment results, they develop individualized treatment plans that outline specific goals, strategies, and measurement systems.
Implementing ABA therapy requires consistency and ongoing data collection. ABA therapists closely monitor progress, make necessary adjustments to the treatment plan, and provide ongoing support and training to parents, caregivers, and educators involved in the individual’s care.
Finding an ABA Therapy Provider
When seeking ABA therapy for yourself or a loved one, it is important to find a qualified and experienced ABA therapy provider. Here are some key factors to consider when selecting a provider:
- Credentials and qualifications: Ensure that the provider has the necessary certifications and qualifications to deliver ABA therapy. Look for credentials such as Board Certified Behavior Analyst (BCBA) or Board Certified Assistant Behavior Analyst (BCaBA).
- Experience and expertise: Consider the provider’s experience in working with individuals with similar needs and goals. Ask for references or testimonials from previous clients to gauge their effectiveness.
- Treatment approach and philosophy: Inquire about the provider’s treatment approach and philosophy to ensure it aligns with your values and goals. Discuss their strategies and techniques to understand how they will address specific behaviors and promote skill development.
- Collaboration and communication: Effective ABA therapy requires collaboration and open communication between the therapist, parents, caregivers, and educators. Ensure that the provider values and promotes collaboration throughout the treatment process.
- Availability and location: Consider the provider’s availability and location, as accessibility and convenience are important factors in ensuring consistent and effective therapy.
Conclusion
Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy is a powerful and evidence-based approach that has proven effective in improving behaviors and promoting skill development in individuals with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) and other developmental disabilities. By understanding the principles and techniques behind ABA therapy, individuals, parents, caregivers, and educators can make informed decisions and play an active role in facilitating positive change.
Whether you are seeking ABA therapy for a loved one or are interested in pursuing a career in the field, the knowledge gained from this article serves as a valuable resource to grasp the essentials of ABA therapy. By recognizing the impact of ABA therapy and its potential to transform lives, we can collectively contribute to creating a more inclusive and supportive society for individuals with ASD and other developmental challenges.